Movement
Detail code for Movement.hpp and Movement.cpp
Declartions of configuration of angle of the car
namespace Movement {
// Servo positions
/*Servo Physical Config on Car in deg
45 90 135
\ | /
\ | /
\|/
0 ------------- 180 */
const uint8_t servoLeft = 45;
const uint8_t servoCenter = 90;
const uint8_t servoRight = 135;
}
Functions of controlling the car movements
Creating the motion by utilizing front, left, right wheel rotations.
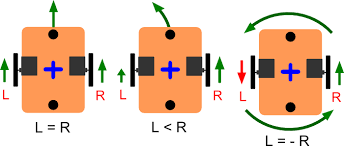
The following function is based on differental drive when L = -R (see the fig.)
In Movement.hpp,
namespace Movement {
void RotateLeft();
void RotateRight();
void MoveForward();
void MoveBackward();
void Stop();
}
void Movement::RotateRight()
@brief Make the car turns right.
void Movement::RotateRight(){
/*The following config is for differential driving, i.e. Front Wheel always 90 deg facing forward */
/*Config. of DC Motor (Side Wheel)*/
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnAntiClockwise(MotorControl::LeftWheel);
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnClockwise(MotorControl::RightWheel);
/*Setting the servo motor to 90 deg */
MotorControl::FrontWheel.TargetAngle = servoCenter;
MotorControl::ServoMotorControl::TurnDeg(MotorControl::FrontWheel);
};
void Movement::Rotateleft()
@brief Make the car turns left.
void Movement::RotateLeft(){
/*The following config is for differential driving, i.e. Front Wheel always 90 deg facing forward */
/*Config. of DC Motor (Side Wheel)*/
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnClockwise(MotorControl::LeftWheel);
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnAntiClockwise(MotorControl::RightWheel);
/*Setting the servo motor to 90 deg */
MotorControl::FrontWheel.TargetAngle = servoCenter;
MotorControl::ServoMotorControl::TurnDeg(MotorControl::FrontWheel);
};
void Movement::MoveForward()
@brief Make the car moves forwards.
void Movement::MoveForward(){
/*The following config is for differential driving, i.e. Front Wheel always 90 deg facing forward */
/*Config. of DC Motor (Side Wheel)*/
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnAntiClockwise(MotorControl::LeftWheel);
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnAntiClockwise(MotorControl::RightWheel);
/*Setting the servo motor to 90 deg */
MotorControl::FrontWheel.TargetAngle = servoCenter;
MotorControl::ServoMotorControl::TurnDeg(MotorControl::FrontWheel);
};
void Movement::MoveBackward()
@brief Make the car moves backwards.
void Movement::MoveBackward(){
/*The following config is for differential driving, i.e. Front Wheel always 90 deg facing forward */
/*Config. of DC Motor (Side Wheel)*/
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnClockwise(MotorControl::LeftWheel);
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::TurnClockwise(MotorControl::RightWheel);
/*Setting the servo motor to 90 deg */
MotorControl::FrontWheel.TargetAngle = servoCenter;
MotorControl::ServoMotorControl::TurnDeg(MotorControl::FrontWheel);
};
void Movement::Stop()
@brief Make the car stops.
void Movement::Stop(){
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::Stop(MotorControl::LeftWheel);
MotorControl::DCMotorControl::Stop(MotorControl::RightWheel);
}
Adjust the speed of motion
Refer to the motor.md, the functions in MotorControl.hpp are used.
Since the struct of the motor (LeftWheel & RightWheel) are created. There is a member in the DCMotor called speed.
By adjusting the speed of LeftWheel & RightWheel, the speed of the movement can be changed.
With PID control
In the .ino, (With PID driver)
For the detail of the PID control, please refer to the PID Section.
The following code is an example of the car moves forwards.
@para LeftWheelPID.target_val Target speed of the leftwheel
@para RightWheelPID.target_val Target speed of the rightwheel
For an instance, both speed of the wheel fixed to 150.0f.
LeftWheelPID.target_val = 150.0f;
RightWheelPID.target_val = 150.0f;
Movement::MoveForward();
vTaskDelay(100/portTICK_PERIOD_MS); //delay for a duration of 100ms
//or use delay(100);
If a faster speed is needed, increase the value of LeftWheelPID.target_val & RightWheelPID.target_val.